In the AWS Shared Responsibility Model, each AWS account owner is responsible for security of his/her account. Nevertheless, AWS does provide several services aimed at identifying potential AWS security threats.
AWS GuardDuty is a machine-learning based AWS service looking for any malicious activity within your AWS account using VPC flow logs, AWS CloudTrail logs, DNS query logs, EKS audit logs, S3 data events and other AWS logs.
The key threats it identifies are:
- Traffic from questionable IP addresses
- Exposed credentials
- Other types of security anomalies, such as:
- the existence of backdoor access
- cryptocurrencies mining
- behavioral anomalies
Whenever Amazon GuardDuty detects a threat, it is reported in its Dashboard. If set up, it can also create an event such as sending a SNS message.
After enabling AWS GuardDuty, it takes between 7 and 14 days to establish the baseline upon which to detect the anomalies.
To enable the service:
- Go to the AWS GuardDuty service in the AWS Console
- If the service has not been yet used, select Enable GuardDuty
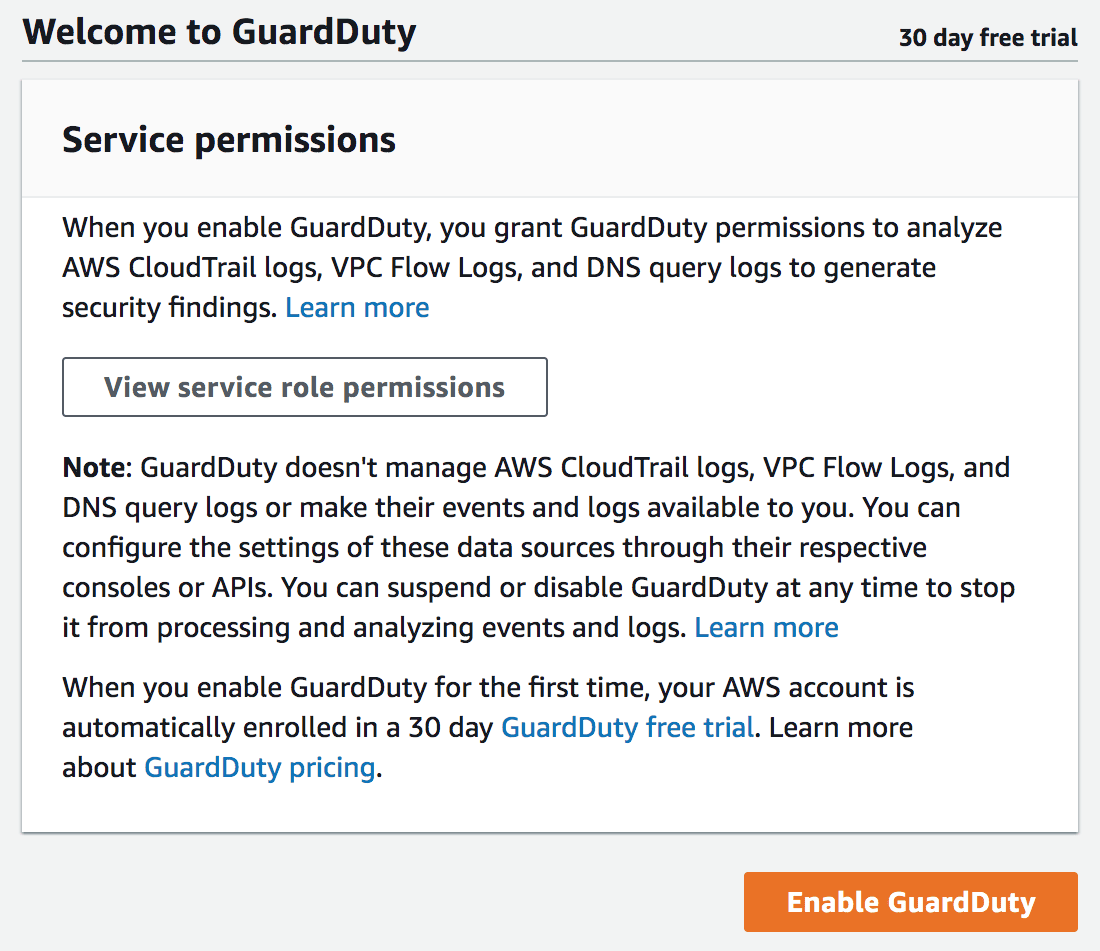
- You can tweak the setup by specifying trusted IPs and CIDR ranges and the list of suspicious IPs and CIDR ranges.
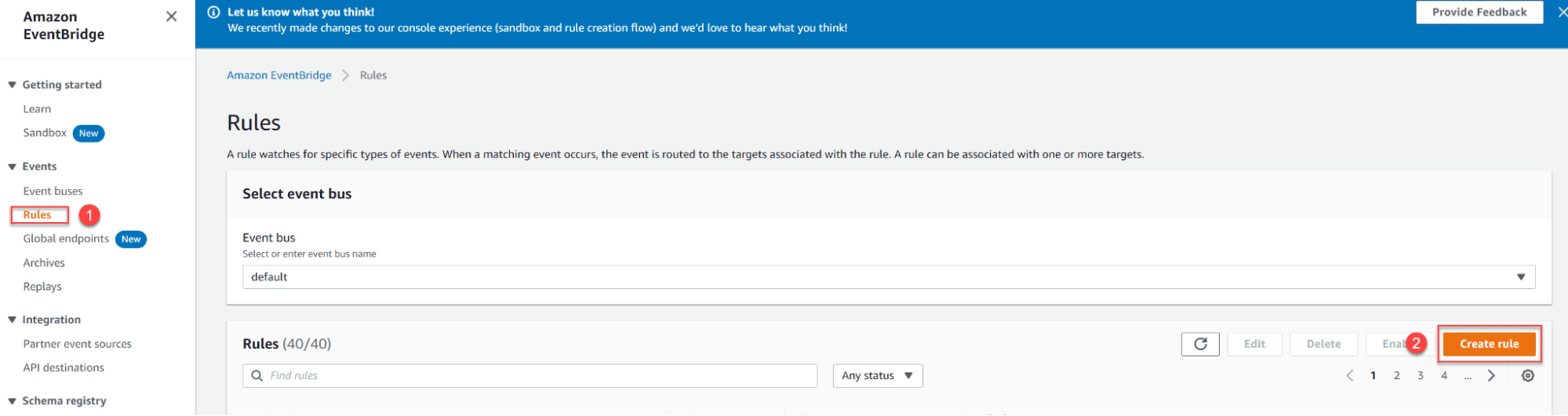
- Set up Amazon EventBridge:
- Go to AWS EventBridge service in the AWS Console
- Create a new rule
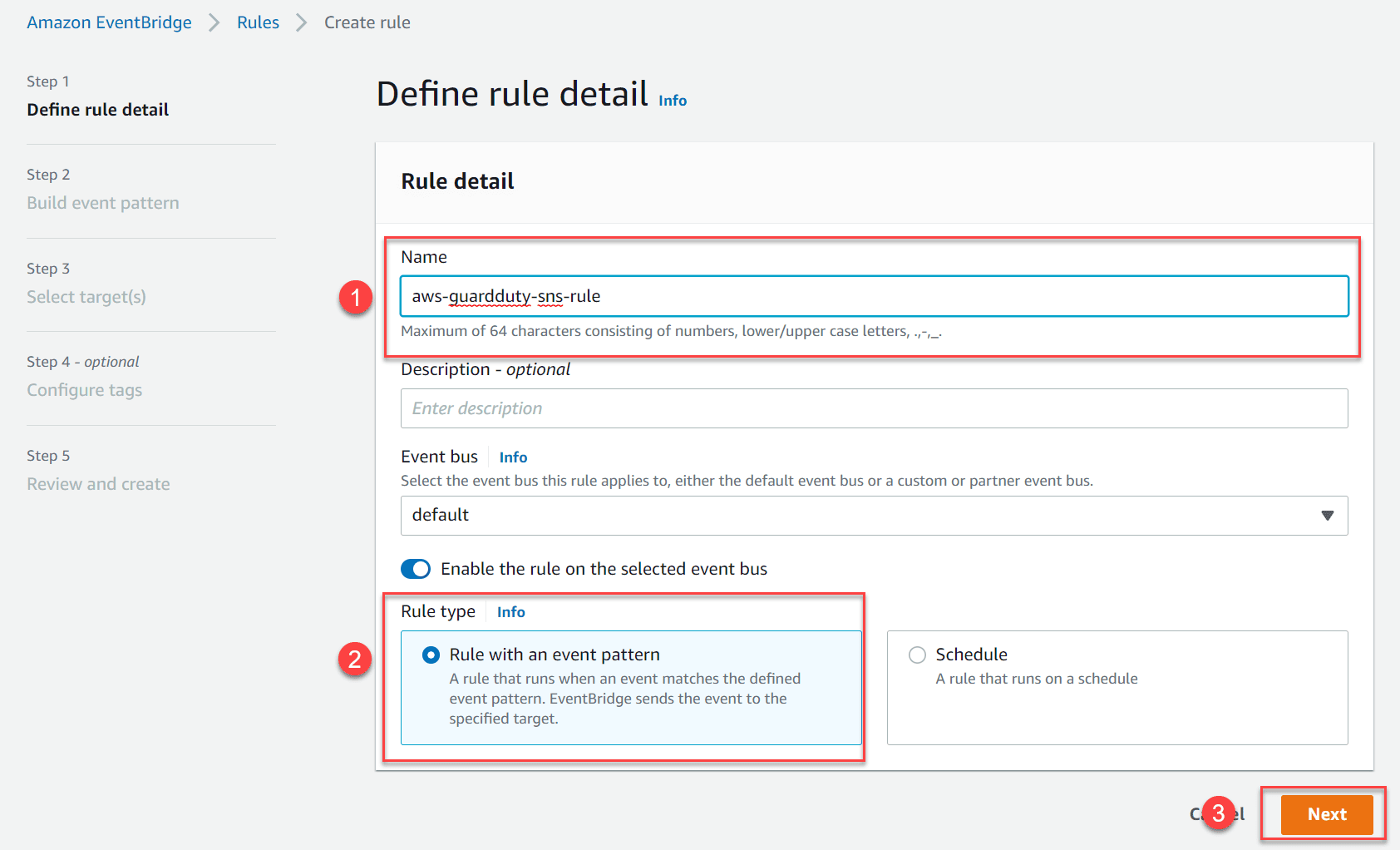
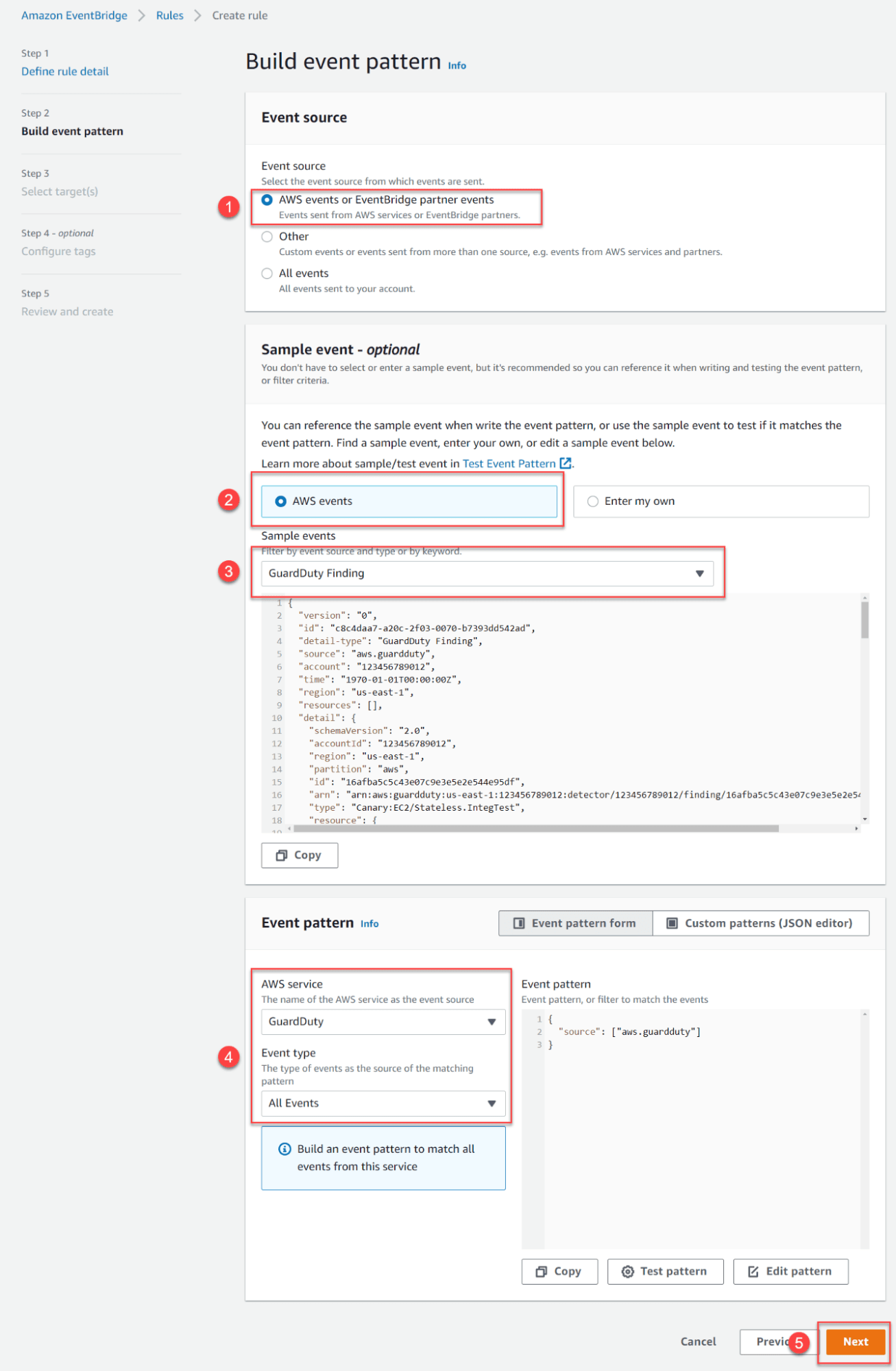
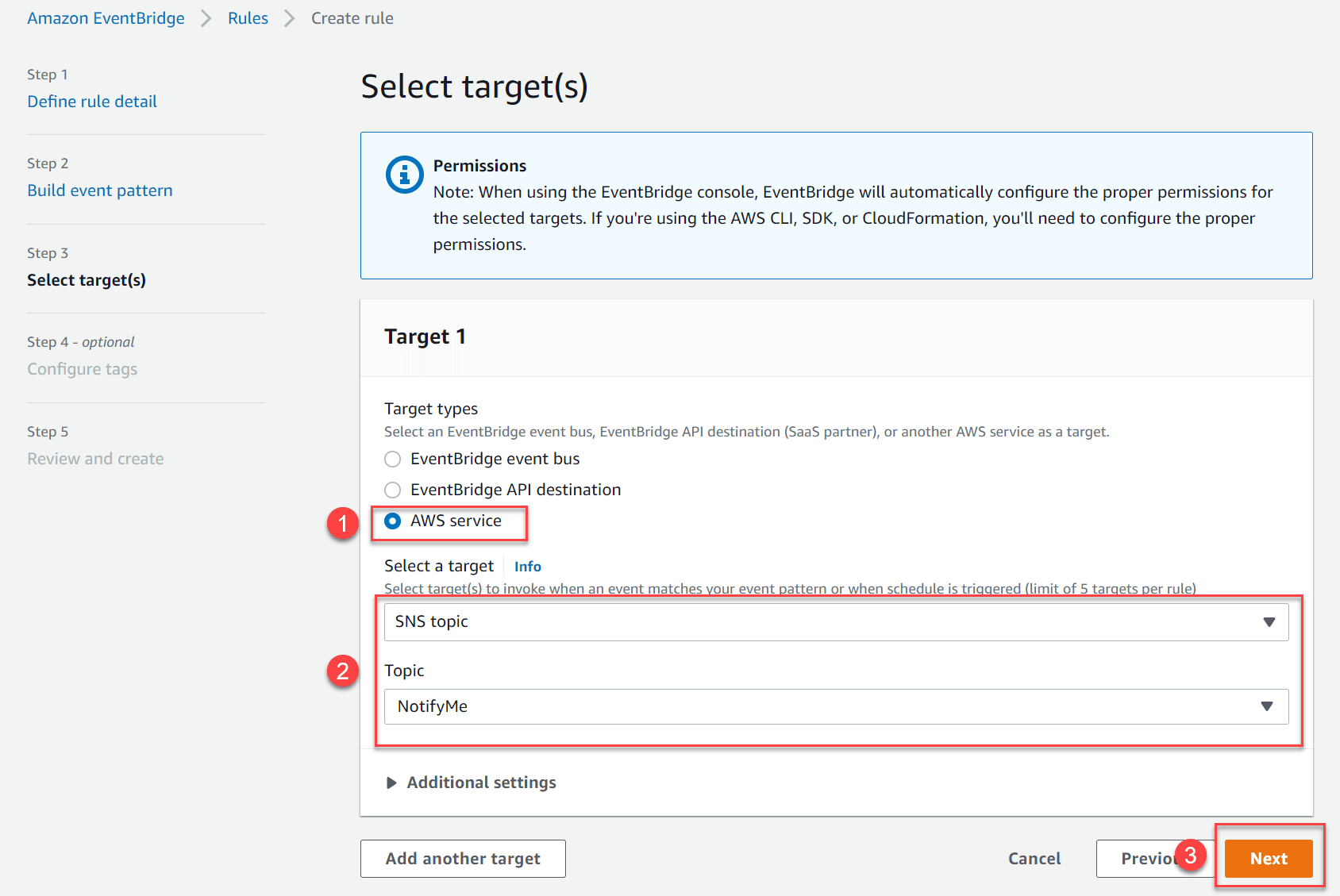
Where the topic is the SNS topic you created for notifications.
Then proceed up to Step 5 – Review and Create.