AWS DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL key-value database service designed for single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. Data in DynamoDB is organized in tables and each table is created in a specific AWS region (AWS DynamoDB also allows Global Tables – see this article for details). For performance and reliability reasons, all data stored in AWS DynamoDB is automatically replicated across a particular region’s availability zones.
AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) is a fully managed object storage service designed for storage and retrieval of any amount of data. Data in S3 is organized in buckets and each bucket is created in a specific AWS region. Similarly to AWS DynamoDB, all data stored in Amazon S3 is automatically replicated across a particular region’s availability zones.
However, most individual resources, such as EC2 or RDS instances, are located in Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). AWS VPC is a logically isolated section of AWS cloud spanning multiple availability zones within a single AWS region.
Since neither AWS DynamoDB, nor AWS S3 is a part of any particular VPC, any traffic from a VPC’s particular resource, such as an EC2 instance, to the AWS DynamoDB / S3 goes via the VPC’s Internet Gateway and then public internet. While this communication uses HTTPS (SSL/TLS) protocol, such a setup is not optimal for security, unnecessary billable AWS Transfer Fees, and public IP addresses costs.
VPC endpoints for DynamoDB and S3 solve these problem:
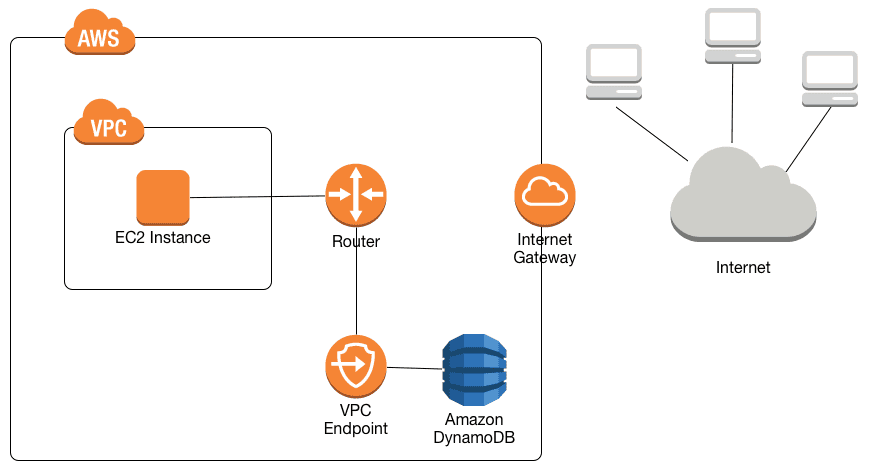
- They allow resources with private IP addresses to communicate with DynamoDB / S3 without exposure to the public internet.
- They do not require any internet gateway, NAT device, or virtual private gateway in your VPC.
Before:
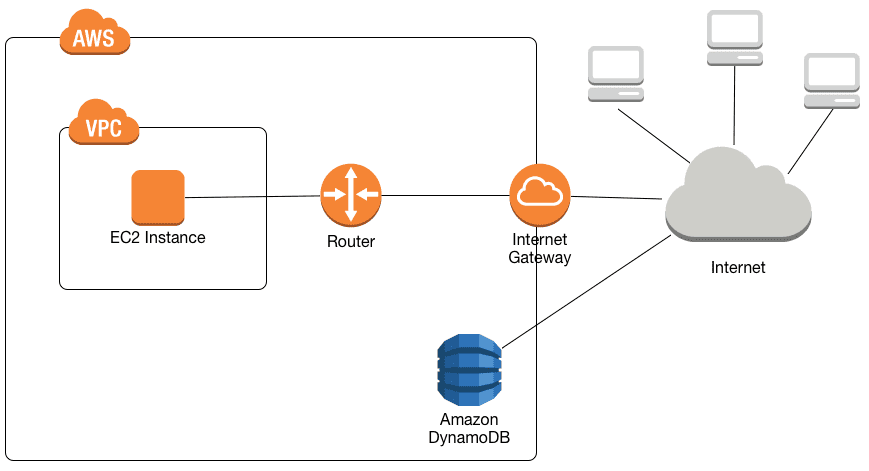
After:
Source for the diagrams: AWS docs
How do you set up a VPC endpoint for DynamoDB/S3?
- For Amazon DynamoDB, follow these steps.
- For Amazon S3, follow these steps.